Melanoma is a dangerous form of skin cancer that has been affecting many Americans in the past few years. In order to generate more awareness among the masses, the American Academy of Dermatology celebrates the month of May as Melanoma Awareness Month. Declared as the National Melanoma Skin Cancer Prevention Month, May is a time dedicated to spreading awareness about skin cancer, its severity, preventive measures as well as the importance of early detection and skin cancer screening. Proper medication and treatment given after timely diagnosis can save precious lives of your loved ones.
My Story
Serendipity has it ways and it certainly did with me. About 7 years back, I ran thirty minutes late for a dermatologist appointment. As a consolation prize for not being able to do the facial peel I was scheduled for, the doctor recommended that, instead, I do my annual skin check-up. Begrudgingly, I consented. I never considered such checkups important and never had done one up to that point. I certainly did not think anything when the doctor took a sample of a tiny mole from my back, until a few days later when I got the news that the biopsy showed I had melanoma. The experience was horrifying to say the least, and that fateful day changed my life forever. Thankfully my diagnosis was at very early stages and I am cancer free. And now my motto is Screening Saves Lives!
Importance of Skin Cancer Screening
Due to the complications associated with the disease, a timely examination and early detection are paramount. For this, full body skin examination is a fundamental tool that helps in the complete screening of a patient’s body and helps in diagnosing any benign marks or cancerous lesions that may turn up hazardous and life threatening in the form of melanoma. Many times these marks go unnoticed by the patients sitting silently to turn up eventually cancerous. More often, even when patients have seen those marks and lesions before examination by a doctor, they were not able to detect them as an early phase of cancer due to lack of awareness and medical background. This further emphasizes the importance of skin examination for cancer screening.
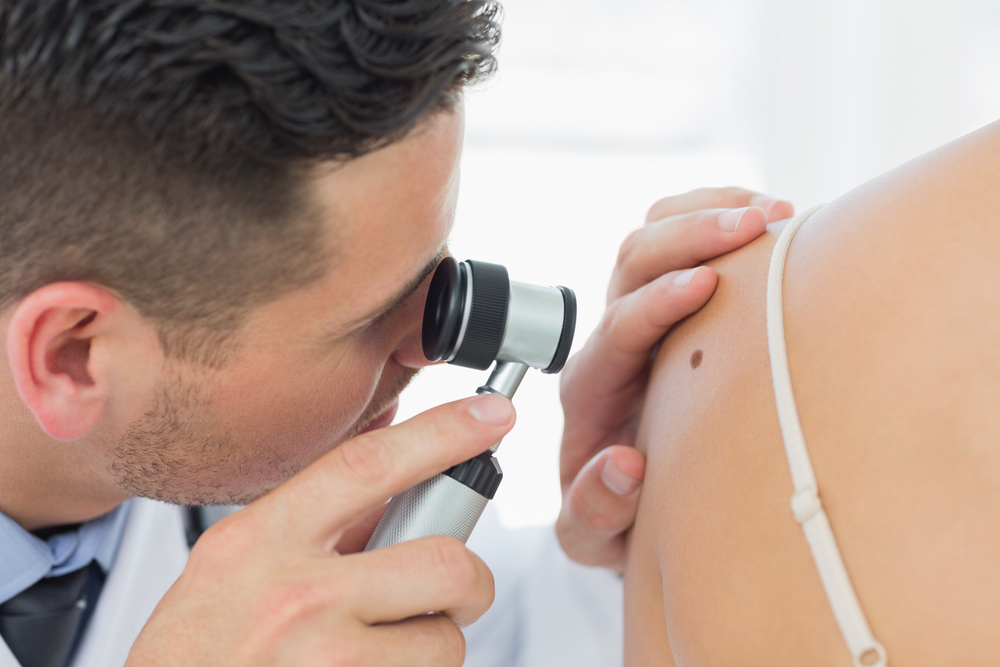
What to expect at skin cancer screenings
Skin cancer screening is done by dermatologists who are experts in diagnosing and managing skin cancer and are equipped with specialized training for the same. In a 10-15 minutes visit, they screen through every part of your skin from head to toe, review your medical history, and address your concerns regarding skin issues. During the skin examination, the dermatologist also informs and educates about how to examine the lesions for a change in color, size, or shape. Any probable change in the moles and lesions need to be reported and examined. This can help you in doing skin checkups at home by yourself in between your appointments with the doctor for complete skin screening. Become a part of the movement by getting a skin screening done for yourself as well as your loved ones. Make an appointment today!
Read more about early detection and self exams here and here







follow me
@notjustapenguin